|
Description
A malignant growth or tumor on the skin that tends
to grow and spread. There are three basic types of skin
cancer, described as follows:
 |
|
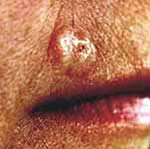
Nodular
Basal Cell Carcinoma
|
|
Basal cell carcinoma, occurring mostly on the
face, neck and hands, is usually a slow-grower and may
be scaly, flat or raised. It often crusts and bleeds,
but does not heal or go away completely.
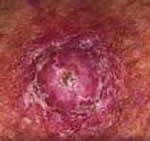
Squamous cell carcinoma, typically appearing
on the face, hands and ears, appears as a reddish/pink
scaly bump. It may begin as a pink or red crusted area.
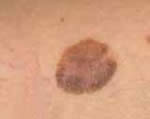
Malignant melanoma is the most serious of skin
cancers. It usually begins as a light brown or flat,
black spot with irregular borders that later can become
red, blue or white. It may start in an existing mole
or as a new flat freckle with irregular borders.
Cause
 |
|
Squamous
Cell Carcinoma
|
|
(Source of information: AAD)
According to the AAD, over exposure to ultraviolet light
(from the sun and indoor tanning lights) is the greatest
risk factor for skin
cancer. They state that ultraviolet radiation causes
almost all cases of basal and squamous cell skin cancer,
and sun exposure is a major cause of skin cancer.
Excessive sun exposure during the early years (birth
through age 18) increases the risk of melanoma by threefold.
Caucasians are 20 times more likely than African-Americans
to develop malignant melanoma. Fair-skinned people have
twice the risk of developing melanoma as olive-skinned
people. Redheads and blondes have a two to four time
increased risk of developing melanoma.
There is an increased risk of nine times for individuals
that have already had one melanoma. People with many
or large moles on their bodies have a substantially
higher risk of melanoma. Those with a history of melanoma
in their family have a higher risk of developing melanoma
themselves.
Who is affected?
 |
|
Early
Superficial
Spreading Melanoma
|
|
One out of every five Americans will develop some form
of skin cancer in their lifetime. Skin cancer
is the most common type of cancer. Half of all cancers
diagnosed is skin cancer. It is estimated that 1 million
new cases of skin cancer will be diagnosed this year
in the United States. Of these, 80% will be basal cell
carcinoma, 16% will be squamous cell carcinoma and 4%
will be melanoma.
In 1998 it is estimated, 1 in 82 Americans have a lifetime
risk of developing melanoma. This increases to 1 in
75 by the year 2000. In 1998 new cases of melanoma increased
by 3% over 1997.
Basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma have a better
than 95% cure rate if detected and treated early.
|